Recently, in reviewing a contract with a demand-side platform (DSP), I came across this typical language in a “Data Ownership” section:
“All Performance Data shall be considered Confidential Information of Advertiser, provided that [VENDOR] may use such Performance Data … to create anonymized aggregated data, industry reports, and/or statistics (“Aggregated Data”) for its own commercial purposes, provided that Aggregated Data will not contain any information that identifies the Advertiser or any of its customers and does not contain the Confidential Information of the Advertiser or any intellectual property of the Advertiser or its customers.” (emphasis added).
I was curious what makes data “anonymized”, and I was even more curious whether the term was casually and improperly used. I’ve seen the same language alternately used substituting “de-identified” for “anonymized”. Looking into this opened a can of worms ….
What are Anonymized and De-Identified Data – and Are They the Same?
Here’s how Gregory Nelson described it in his casually titled “Practical Implications of Sharing Data: A Primer on Data Privacy, Anonymization, and De-Identification”:
“De-identification of data refers to the process of removing or obscuring any personally identifiable information from individual records in a way that minimizes the risk of unintended disclosure of the identity of individuals and information about them. Anonymization of data refers to the process of data de-identification that produces data where individual records cannot be linked back to an original as they do not include the required translation variables to do so.” (emphasis added)
Or in other words, both methods have the same purpose and both methods technically remove personally identifiable information (PII) from the data set. But while de-identified data can be re-identified, anonymized data cannot be re-identified. To use a simple example, if a column from an Excel spreadsheet containing Social Security numbers is removed from a dataset and discarded, the data would be “anonymized”.
But first … what aspects or portions of data must be removed in order to either de-identify or anonymize a set?
But What Makes Data “De-Identified” or “Anonymous” in the First Place?
Daniel Solove has written that, under the European Union’s Data Directive 95/46/EC, “Even if the data alone cannot be linked to a specific individual, if it is reasonably possible to use the data in combination with other information to identify a person, then the data is PII.” This makes things complicated in a hurry. After all, in the above example where Social Security numbers are removed, remaining columns might include normally non-PII information such as zip codes or gender (male or female). But the Harvard researchers Olivia Angiuli, Joe Blitzstein, and Jim Waldo show how even these 3 data points in an otherwise “de-identified” data set (i.e. “medical data” in the image below) can be used to re-identify individuals when combined with an outside data source that shares these same points (i.e. “voter list” in the image below):
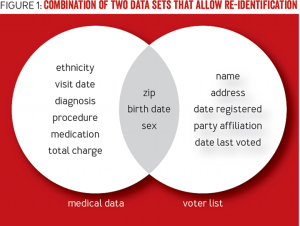
(Source: How to De-Identify Your Data, by Olivia Angiuli, Joe Blitzstein, and Jim Waldo, http://queue.acm.org/detail.cfm?id=2838930)
That helps explain the Advocate General opinion recently issued in the European Union Court of Justice (ECJ), finding that dynamic IP addresses can, under certain circumstances, be “personal data” under the European Union’s Data Directive 95/46/EC. The case involves interpretation of the same point made by Daniel Solove cited above, namely discerning the “personal data” definition, including this formulation in Recital 26 of the Directive:
“(26) … whereas, to determine whether a person is identifiable, account should be taken of all the means likely reasonably to be used either by the controller or by any other person to identify the said person …”
There was inconsistency among the EU countries on the level of pro-activity required by a data controller in order to render an IP address “personal data”. So, for example, the United Kingdom’s definition of “personal data”: “data which relate to a living individual who can be identified – (a) from those data, or (b) from those data and other information which is in the possession of, or is likely to come into the possession of, the data controller” (emphasis added). Not so in Germany and, according to a White & Case report on the ECJ case, not so according to the Advocate General, whose position was that “the mere possibility that such a request [for further identifying information] could be made is sufficient.”
Which then circles things back to the question at the top, namely: Are Anonymized and De-Identified Data the Same? They are not the same. That part is easy to say. The harder part is determining which is which, especially with the ease of re-identifying presumably scrubbed data sets. More on this topic shortly.
Read More


